Name: _______________________________
In math courses at the national campus Spring 2001 the campuswide population mean grade
point average (GPA) m was 1.613. During the Spring 2001
term at the national campus 15 Yapese male students attained a sample mean GPA ![]() of 1.133 with a standard deviation sx of 1.407
in math courses. At an alpha a of 0.1, is the Yapese male
math GPA statistically significantly lower than the national campus math GPA?
of 1.133 with a standard deviation sx of 1.407
in math courses. At an alpha a of 0.1, is the Yapese male
math GPA statistically significantly lower than the national campus math GPA?
| Statistic | Equations | Excel |
|---|---|---|
| Square root | =SQRT(number) | |
| Sample size | n | =COUNT(data) |
| Sample mean | =AVERAGE(data) | |
| Population mean | m x P(x) n p (binomial) |
=AVERAGE(data) |
| Sample standard deviation | sx |
=STDEV(data) |
| Population standard deviation | s |
=STDEVP(data) |
| Slope | =SLOPE(y data, x data) | |
| Intercept | =INTERCEPT(y data, x data) | |
| Correlation | =CORREL(y data, x data) | |
| Binomial probability | = nCr pr q(n-r) | =COMBIN(n,r)*p^r*q^(n-r) |
| Calculate a z value from an x | z = |
=STANDARDIZE(x, m, s) |
| Calculate an x value from a z | x = s z + m | |
| Calculate a z value from an |
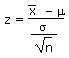 |
=STANDARDIZE(x, m, s/SQRT(n)) |
| Find a probability p from a z value | =NORMSDIST(z) | |
| Find a z value from a probability p | =NORMSINV(p) | |
| Standard error of the population mean | ||
| Standard error of the sample mean | ||
| Determining z critical zc from a for confidence intervals or two-tail tests. | =NORMSINV(1-a/2) | |
| Error tolerance E of a mean for n ³ 30 using s | =CONFIDENCE(a,s,n) | |
| Error tolerance E of a mean for n ³ 30 using sx | E = |
=CONFIDENCE(a,sx,n) |
| Error tolerance E of a mean for n < 30. Can also be used for n ³ 30. | [no Excel function, determine tc and then multiply by standard error of the mean as shown in the equation] | |
| Determining tc from a and the degrees of freedom df for a confidence interval or a two-tail test. | =TINV(a,df) | |
| Calculate an |
||
| Calculate a confidence interval for a population mean m from
a sample mean |
||
| Determining zc from a for a two-tail hypothesis test. | =NORMSINV(a/2) [returns only the negative value for zc] |
|
| Determining zc from a for a one-tail hypothesis test. | =NORMSINV(a) [returns the right tail zc, change the sign for the left tail] |
|
| Determining tc from a and degrees of freedom df for a two-tail hypothesis test. | =TINV(a, df) [returns only the positive value for tc] |
|
| Determining tc from a and degrees of freedom df for a one-tail hypothesis test. | =TINV(2a, df) [returns only the left-tail tc, change the sign for right-tail] |
|
| Determining the one-tail p-value for a z-statistic z for a negative value of z | =NORMSDIST(z) | |
| Determining the one-tail p-value for a z-statistic z for a positive value of z | =NORMSDIST(1-z) | |
| Determining the two-tail p-value for the absolute value of the z-statistic | =2*NORMSDIST(1-|z|) | |
| Determining the one-tail p-value for a t-statistic t and degrees of freedom df | =TDIST(t,df,1) [TDIST accepts only positive values for t, use the absolute value of t] |
|
| Determining the two-tail p-value for a t-statistic t and degrees of freedom df | =TDIST(t,df,2) |