- Chrysophyta
- Cycadophyta
- Gingkophyta
- Lycopodophyta
- Pinophyta

Sections:
Multiple Choice
Matching
Short answer
1. A botanist who identifies two plants as being the same species because
"they look alike" is using
|
2. A new species originates in…
|
3. In terms of evolutionary survival, a "winner species" is
that in which individuals
|
4. Which of the following is taken as evidence of evolution?
|
5. Natural selection presumes that...
|
6. Speciation that has occurred on the mountain tops of Pohnpei is most
likely due to:
|
7. Morphological plasticity mean that a species...
8. A tetraploid hybrid has...
|
9. Cyanobacteria can contain
|
10. Cyanobacteria get their characteristic color from
|
11. The nitrogen fixing nodule in Cyanobacteria is called a
|
12. A botanical fairy ring is
13. In a mycorrhizal association with plantae, fungi typically provide to
the plant roots:
|
14. The phrase "we are immortal in our genes" refers to:
|
15. In terms of evolutionary success, a long life is only beneficial if...
16. Fungal hyphae...
17. Giant kelp is held to the ocean floor by
|
18. If you take a blade of algae and rub it on your face for ten
minutes and wind up with your face covered in slimy mucilage, then you have most likely
found a:
|
19. On the beaches of Kosrae there occasionally washes up these masses of small brown leaves with little white balls. This algal material floats on the surface of the ocean. It is a member of:
|
 |
20. The shown leaf is from:
|
 |
21. How do plants conserve water during dry conditions?
22. C4 plants avoid a problem that plagues C3 plants, a problem associated with photosynthezing during conditions under which the plant must conserve water, what problem does the C4 mechanism circumvent?
23. At the very center of the reaction center of chlorophyll is a single
atom of:
|
24. The color of carotenoids is:
|
25. The antenna complex is designed to:
|
26. To close its leaves when they are touched, Mimosa pudica uses:
|
27. At the core of scientific methods is the concept...
28. What is wrong with the statement, "the moon is populated by little green men who can read our minds and will hide whenever anyone on the Earth looks for them, and will flee into deep space whenever a spacecraft comes near"?
29. Taxonomy is the study of
|
30. Hexhead elatus is a
|
31. "Fixing" nitrogen means
|
32. Life can survive at -45°F.
|
33. Archegonia are the
|
34. Antheridia are the
|
35. Does natural selection create new genes that increase the adaptivity
of the plant to its environment?
|
36. Tonight when I am be drinking the sacred root there will stuff in the
cup that is real slimey and goopy. What is the source of this mucous-like substance?
|
| 37. Cinnamon comes from:
|
38. In what phase do bryophytes spend most of their life?
|
| 39. Do bryophytes contains hormones such as auxin?
|
40. Are there bryophytes that reproduce asexually?
|
| ____ 41. | Ascomycetes | a. | Eukartyotic brown algae |
| ____ 42. | Basidiomycetes | b. | Eukartyotic green algae |
| ____ 43. | Chlorophyta | c. | Eukartyotic red algae |
| ____ 44. | Chloroxybacteria | d. | Eukaryotic with elaborate spore containers |
| ____ 45. | Cyanobacteria | e. | Eukaryotic with peglike spore structures |
| ____ 46. | Deuteromycetes | f. | Eukaryotic with saclike spore structures |
| ____ 47. | Phaeophyta | g. | Eukaryotic without sexual reproduction |
| ____ 48. | Rodophyta | h. | Prokaryotic with phycobillins |
| ____ 49. | Zygomycetes | i. | Prokaryotic with similarity to chloroplasts |
| j. | Prokaryotic with chitinous cells walls |
| ____ 50. | Club and spike mosses | a. | Acrocarpus |
| ____ 51. | Ferns | b. | Lycopodophyta |
| ____ 52. | Mosses with an erect growth habit, main stem is of limited length | c. | Pleurocarpus |
| ____ 53 | Mosses with a matlike growth habit, main stem is of unlimited length | d. | Pteridophyta |
| ____ 54 | Abscissic acid | A. | Carries carbohydrates |
| ____ 55 | Auxin | B. | Carries water and minerals |
| ____ 56 | Cytokinins | C. | Inhibits growth |
| ____ 57 | Ethylene | D. | Promotes cell division |
| ____ 58 | Gibberillins | E. | Promotes internode elongation |
| ____ 59 | Phloem | F. | Ripens fruit |
| ____ 60 | Xylem | G. | Stimulates apical growth |
61. What is the name of the faulty theory that would make the following prediction: "If you read many books and study very hard throughout your life, your children will be smarter."
62. Why are mosses so small?
63. Why are mosses so wet?
64. What features distinguish the bryophytes from the ferns of pteridophyta?
65. Is the Australian pine, Casuarina equisetifolia, a gymnosperm in Pinophyta?
66. Why is the Australian pine, Casuarina equisetifolia, a gymnosperm in Pinophyta OR Why is the Australian pine, Casuarina equisetifolia, not a gymnosperm in Pinophyta?
66. Are there any 80 million year old Gingko trees that are alive now?
67. Is the Cook Pine, Araucaria columnaris, a gymnosperm?
68. Do gymnosperms have flowers?
69. What color is the flower of the Cook Pine, Araucaria columnaris?
70. Plants go through a complex chemical process when converting sugars and starches to energetic electrons. These energetic electrons power the production of ATP and NADPH, the energy currency of cells. The electrons, once depleted of energy, are finally "donated" to Oxygen. Why can't plants simplify by directly oxidizing the sugars and starches?
71. By what process do cells convert sugars and starches to alcohol?
72. Some plants have red leaves due to the presence of red xanthophylls. Xanthophylls are oxidized carotenoids found in the antenna complexes of the photosystem. What is the function of these xanthophylls in the antenna complexes?
73. Mature, fully formed chloroplasts need only three inputs to do their daily work of generating sugars and starches. Name the three inputs.
74. What is the rhizosphere?
75. From what type of plant tissue are Louisville Sluggers made?
76. What, botanically speaking, is a sucker?
77. Is sugar cane a monocot or dicot?
78. How do we know whether sugar cane is a monocot or a dicot just by inspection of the structure of the stem (or by eating it!)
79. Do plants use oxygen for respiration?
80. What are the chemical inputs necessary for respiration?
81. Why do plants respire at all – why not simply create ATP by photosynthesis whenever energy is needed?
82. When plants respire anaerobically, two possible results are "bread rises" and "people can get stupid." What are the chemical compounds produced by anaerobic plant respiration?
83. Who or what is Roy G. Biv?
84. What is the physical, optical, explanation for the green coloration of plants?
85. Why would a plant want to be black?
86. What are the daily outputs of photosynthesis?
87. Name a plant that uses its above ground stem as its primary storage for sugars.
88. What is a stolon?
89. What is the function of stoma?
90. What is the common English name for Artocarpis altilis?
91. What is the common English name for Cordyline fruticosa?
92. What is the botanical names for the fruit type of a coconut?
93. Miracle-Gro™ for tomatoes plant food (fertilizer) is marked as being "18-18-21." What do the numbers mean and what specific nutrient does each number represent?
94. What are knots in wood?
95. What is Seasonal Affective Disorder?
96. What houseplant can you grow that will be a natural humidifier of the air in winter?
97. What is self-compatibility?
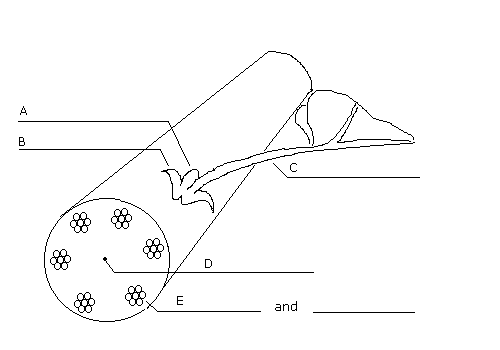
98. Correctly label the identified items below:
99. Label the listed items on the one of the following two images. Both images are of the same flower.

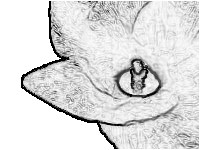
100. Label the listed items on any one of the following three images. All three images are of the same flower.



101. On the following cutway of an ivory nut label the exocarp, mesocarp, and endocarp layers.

102. Fill in the four blank cells on the chart below: